Server Replication vs. Backup: What’s the Difference?
Your business relies on data to operate smoothly, and when systems fail or files are corrupted, the consequences can be significant. Two common methods used to protect data are server replication and backup. These terms are often confused with each other, but they serve very different purposes. Understanding the difference helps you build a more reliable and secure IT environment.
What Is Server Replication?
Server replication is the process of continuously copying data from one server to another in real time or with a slight delay. The goal is to keep a second server ready to take over if the primary one becomes unavailable.
How It Works
The secondary server receives updates continuously from the primary server.
It acts as a live copy, so operations can continue with minimal interruption.
Types of Replication
Synchronous replication copies data instantly before a transaction is completed. This reduces data loss but may affect performance.
Asynchronous replication sends updates with a small delay. This offers better performance but may result in a small amount of data loss during failover.
Ideal Use Cases
Businesses that require systems to be available at all times
Workloads where downtime interrupts operations
Multi-site setups that require consistent data across locations
Environments running mission-critical databases and applications
What Is Backup?
Backup is a method of creating a point-in-time copy of your data. Backups are stored separately and can be used to restore systems after an incident. Unlike replication, backups are not continuous. They follow a schedule and keep multiple versions of your data.
How Backups Work
Scheduled snapshots are saved to dedicated storage such as the cloud or an offsite location.
Backups may include:
Full backups which copy all data
Incremental backups which capture changes since the last backup
Differential backups which record changes since the last full backup
Ideal Use Cases
Recovering from ransomware or malware
Restoring deleted or corrupted files
Long-term data retention
Meeting audit and compliance requirements
Cost-effective recovery planning
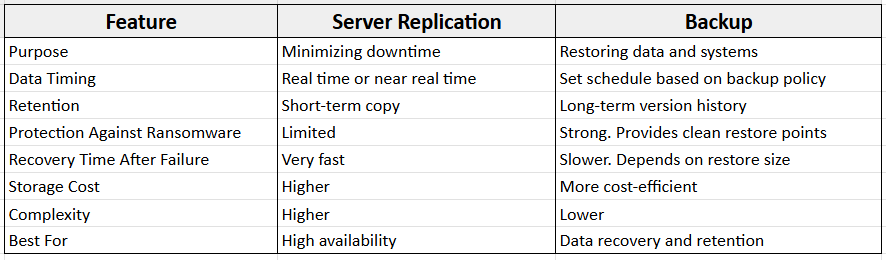
Server Replication vs. Backup: Key Differences
When Should You Use Server Replication?
Server replication is suited for environments where uptime is a high priority. Use replication if you need to:
Keep operations running with minimal disruption
Maintain live copies of critical applications
Support systems that cannot afford lengthy downtime
Provide fast failover between locations or systems
When Should You Use Backup?
Backup is essential when you need the ability to restore clean, historical copies of your data. Use backups if you need to:
Recover from ransomware or accidental deletion
Restore files from previous versions
Meet legal or compliance retention rules
Manage recovery without the cost of a full secondary environment
Do You Need Both Replication and Backup?
Yes. Replication and backup address different risks. Replication keeps systems running, but it also copies errors, corrupted files, or ransomware to the secondary server. Backups provide clean restore points that allow you to recover data safely.
Using both gives your business:
High availability
Complete recovery options
Protection against ransomware
Access to long-term data history
Common Misconceptions
"Replication works the same way as backup."
Replication mirrors data but does not store older versions.
"Real-time data syncing protects against ransomware."
It does not. Replication copies infected files instantly.
"Replication provides long-term retention."
Only backups support long-term retention and versioning.
"One solution is enough."
Most businesses need both to protect data and maintain continuity.
How SMBs Can Choose the Right Setup
Before choosing a solution, consider the following:
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) which defines how much data you can afford to lose
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) which defines how quickly systems must be restored
Budget and available resources
Compliance or retention requirements
Your level of risk from threats such as ransomware
Most businesses benefit from a combined approach that uses replication for availability and backups for recovery and protection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Infrastructure
Server replication and backup serve distinct but complementary roles in protecting your business data. Replication keeps your systems running during unexpected failures, ensuring minimal downtime. Backup provides secure restore points, allowing you to recover clean and historical data when needed.
Using both strategies together creates a strong, resilient infrastructure that safeguards your business against data loss, ransomware, and operational interruptions.
If you want expert guidance on designing the right data protection setup for your business, our team can provide a tailored assessment and recommend the best approach for your infrastructure.